Information disclosure
Information disclosure: Information disclosure, also known as information leakage, is when a website unintentionally reveals sensitive information to its users.
How to test for information disclosure vulnerabilities:
3.Using Burp’s engagement tools
4.Engineering informative responses
Check for information disclosure:
robots.txt
Source code,path analysis
Default file(phpinfo,login,admin,.git)
method check(GET,PUT,TRACE,POST,OPTIONS)
Basic Example of IDV:
1.Revealing the names of hidden directories, their structure, and their contents via a robots.txt file or directory listing. 2.Providing access to source code files via temporary backups. 3.Explicitly mentioning database table or column names in error messages. 4.Unnecessarily exposing highly sensitive information, such as credit card details. 5.Had-coding API keys, IP addresses, database credentials , and so on in the source code. 6.Hinting at the existence or absence of resources, usernames, and so on via subtle differences in application behaviour.
How do IDV arise:
1.Failure to remove internal content from public content. 2.Insecure configuration of the website and related technologies. 3.Flawed design and behaviour of the application.
Tools: Burpsuite
Description: This lab’s verbose error messages reveal that it is using a vulnerable version of a third-party framework. To solve the lab, obtain and submit the version number of this framework.
Firstly access the lab and intercept the burpsuite.After intercept the burpsuite we change the product id.
GET /product?productId=1 HTTP/2
Instead of number we used strings and repeater mode.Then send the request.The response was internal server error .
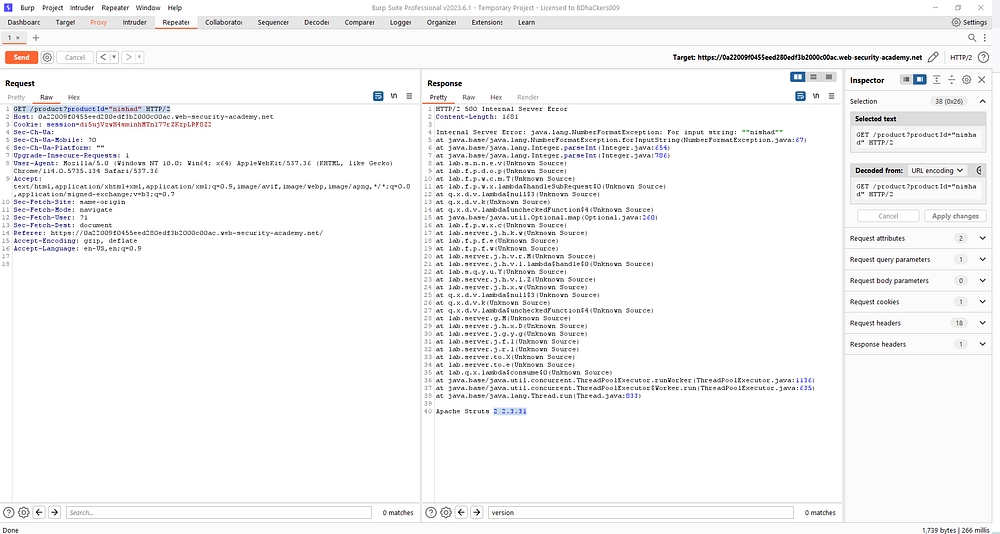
GET /product?productId=”nishad” HTTP/2
after change the parameter it shows the server version 2.2.3.31
#Lab-2 : Information disclosure on debug page.
Description: This lab contains a debug page that discloses sensitive information about the application. To solve the lab, obtain and submit the SECRET_KEY environment variable.
Tools: Burpsuite
To automate hunting for comments, you can use Burp:
Navigate to Target and select Site Map.
Right click the correct target, select Engagement Tools, and select Find Comments.
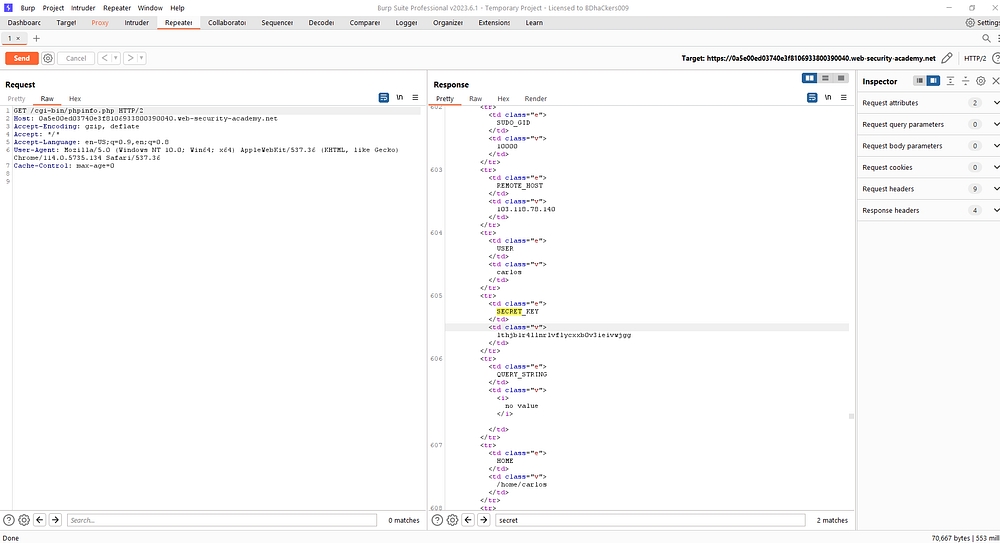
/cgi-bin/phpinfo.php
Then send the request in repeater & the response was ok.The secret key was lthjb1r4llnrlvflycxxb0v3ieivwjgg.
#Lab-3 : Source code disclosure via backup files.
Description: This lab leaks its source code via backup files in a hidden directory. To solve the lab, identify and submit the database password, which is hard-coded in the leaked source code.
Firstly check the robots.txt file and see the /backup file is disallow.Then check /backup file the source code are visible and password was given.The password was : oifs3ta0y6fkjk8d2ql5k2l7wp0ywk7h
Then submit the password the lab is solved.
#Lab-4 : Authentication bypass via information disclosure.
Description: This lab’s administration interface has an authentication bypass vulnerability, but it is impractical to exploit without knowledge of a custom HTTP header used by the front-end.
To solve the lab, obtain the header name then use it to bypass the lab’s authentication. Access the admin interface and delete the user carlos.
You can log in to your own account using the following credentials: wiener:peter
Firstly login username:wiener & password:peter and intercept the burpsuite.
GET /product?productId=2 HTTP/2 check the method.Apply TRACE method and used “/admin”
TRACE /admin HTTP/2
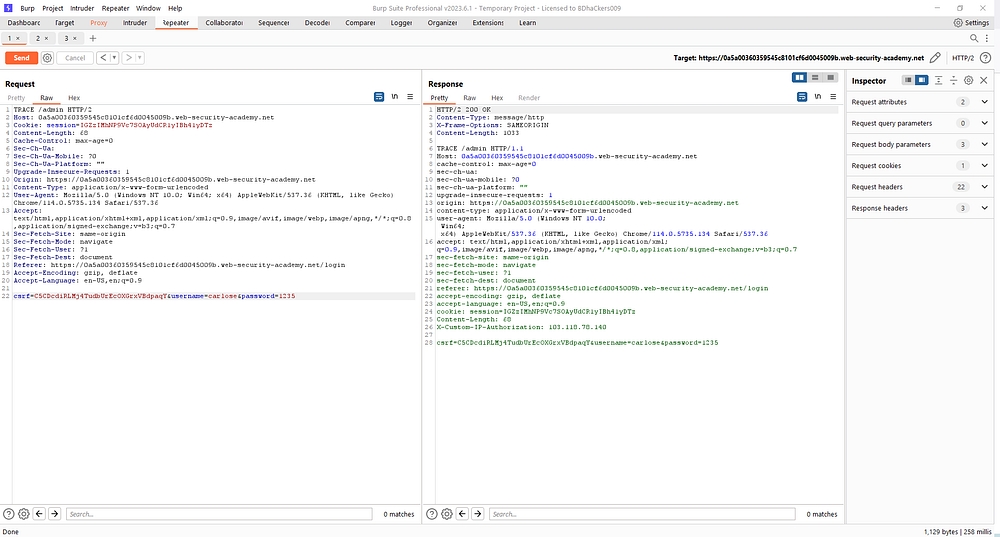
TRACE method used for only debugging.After that it shows
X-Custom-IP-Authorization: 103.118.78.140 & expose the critical information.
After change the TRACE method we used GET method.GET method show only data.Then we send the data in the browser.
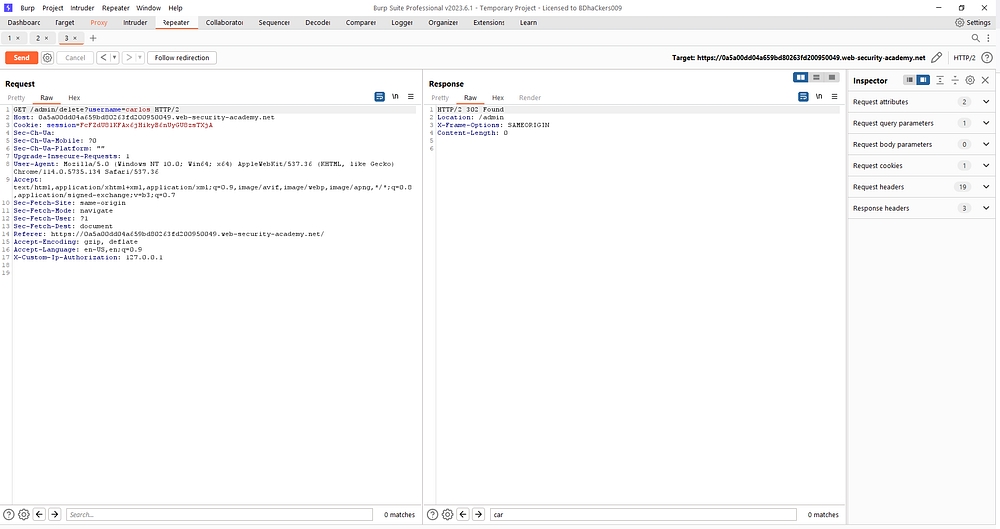
Solve the lab.congratulations
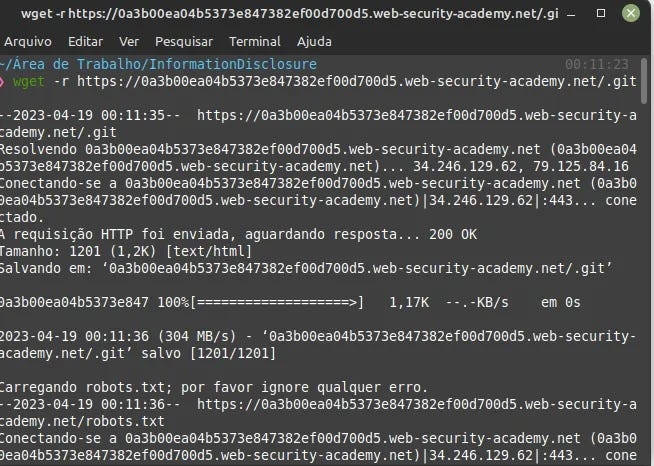
#Lab-4 : Information disclosure in version control history.
Description: This lab discloses sensitive information via its version control history. To solve the lab, obtain the password for the administrator user then log in and delete the user carlos.
wget -r https://0a1c009704343dd680b63055008500fe.web-security-academy.net/.git
Last updated