Clear Text Transmission Of Sensitive Data
Some applications transmit passwords over unencrypted connections, making them easy targets for interception. Attackers can exploit this by eavesdropping on network traffic, especially over public Wi-Fi, corporate, or home networks with compromised devices.
Many communication channels can be sniffed by anyone with network access, making exploitation remarkably easy.
We've all seen HTTP vs. HTTPS, but many don’t realize the difference. If your website handles logins, transactions, or user data, HTTPS is a must. If it's purely static (no sensitive interactions), HTTP may be fine—but HTTPS is still recommended for security and trust.
Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS
HTTP :
An application-layer protocol for communication between web browsers and servers.
Lacks data integrity—attackers can tamper with transmitted data.
Transmits data in plaintext, making it readable to anyone intercepting the traffic.
HTTPS :
Encrypts communication to protect data integrity and privacy.
Prevents attackers from tampering with data exchanged between websites and users.
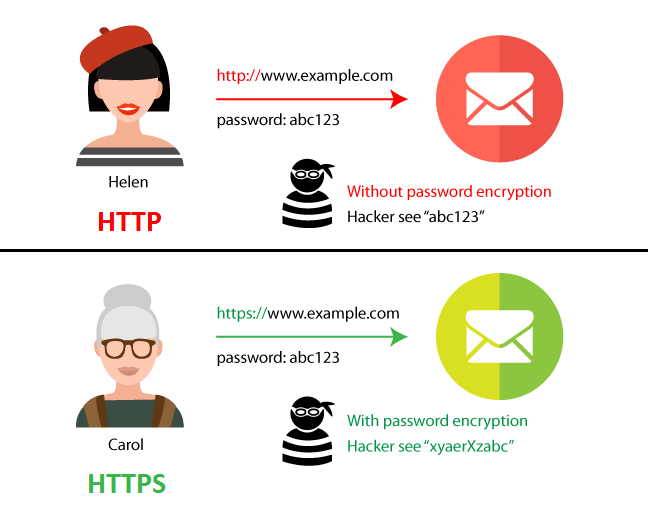
HTTPS uses SSL/TLS encryption, which secures data with a public key (widely known) and a private key (kept secret by the recipient).

How to find this vulnerability ?
Your target website is using http on the login panel
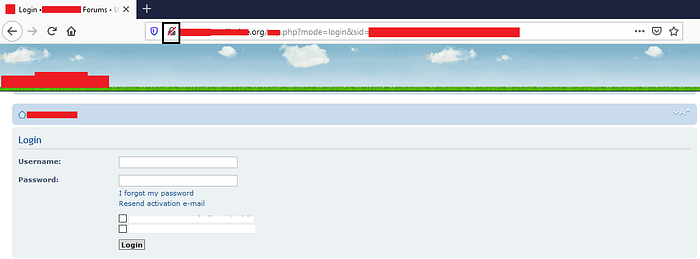
2. Start WireShark for intercepting traffic
Here I have selected Wi-Fi because my PC is connected to Wi-Fi
3. Start packet capturing in WireShark and login to your website
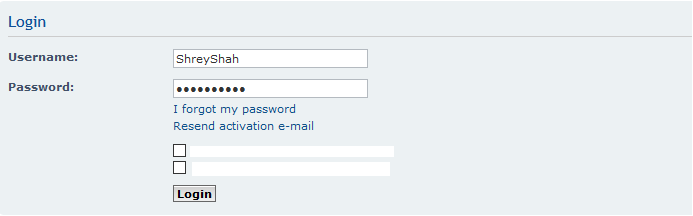
Here you can see the username but the password is hidden, let’s check in the WireShark.
4. Go to WireShark and apply this filter : http.cookie
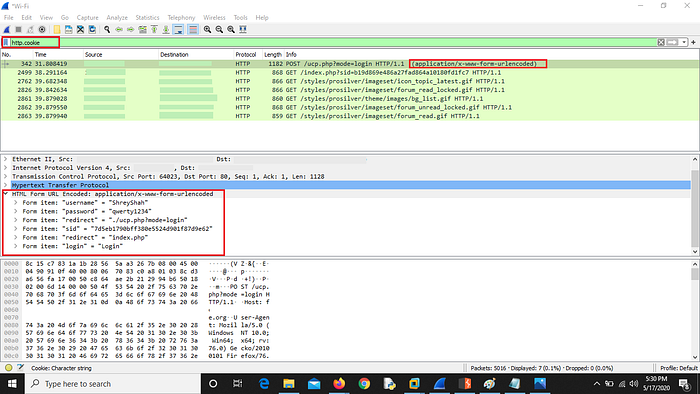
Any attacker can steal the sensitive information if he/she is in the network.
So this was simple and known to many people but what if every GET request is secured ? The website you visit is using HTTPS, so now what to do ? Have you ever tried for POST request ? Let’s Check it.
On the same website I saw the page was having https://www.website.com but when I intercepted the request using burp suite and I saw the POST request for saving the data was using HTTP protocol and I again intercepted it using WireShark and every thing was visible
Exploiting POST Method :
Your website is using HTTPS for every GET request
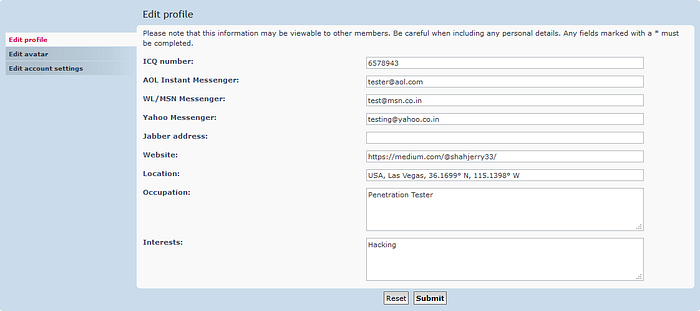
This page was using HTTPS when you visit it. Now this is private information which is visible to user itself but not to an attacker as the GET request is secure by HTTPS protocol
2. Fill the form and Intercept the request using burp suite to check if the POST request is using HTTPS or HTTP for saving or transferring data
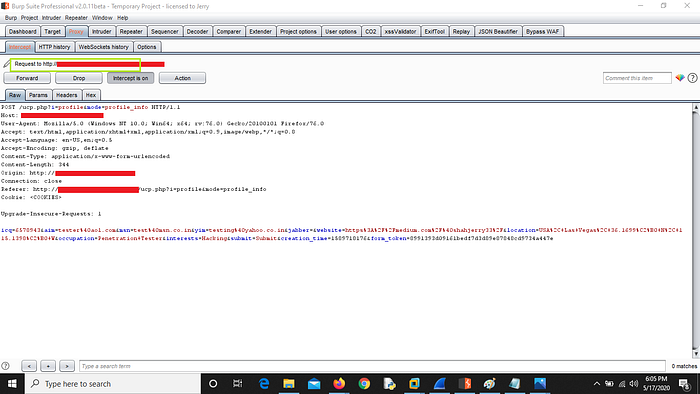
3. Now check WireShark logs for the same request using same filter : http.cookie
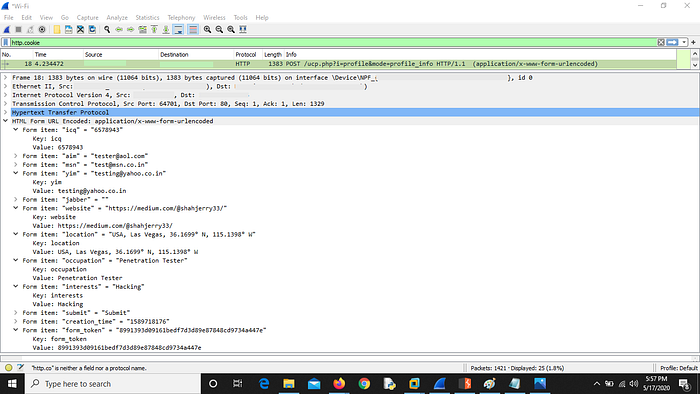
NOTE : You can perform this attack on POST requests like changing password, sending messages, publishing private post, transferring payments etc.
Reports :
https://hackerone.com/reports/214571https://hackerone.com/reports/813159 https://hackerone.com/reports/2337938 https://hackerone.com/reports/1987680https://hackerone.com/reports/173268 https://hackerone.com/reports/1565622https://hackerone.com/reports/1213181 https://hackerone.com/reports/1730660https://hackerone.com/reports/751581 https://hackerone.com/reports/2129769
Last updated