CRLF Injection
Getting Started
Now, What is CRLF?
feed = \n (%0a)
Carriage Return = \r (%0d)Basically, Pressing Enter key is the combination of carriage return & line feed
Windows Editor mostly uses a combination of \r\n Unix uses mostly
Diggin' into Injection and Attack Vector
What is CRLF Injection?
A Carriage Return Line Feed (CRLF) Injection vulnerability occurs when an application does not sanitize user input correctly and allows for the insertion of carriage returns and line feeds, input which for many internet protocols, including HTML, denote line breaks and have special significance. For example, Parsing of HTTP message relies on CRLF characters (%0D%0A which decoded represent \r\n) to identify sections of HTTP messages, including headers. Reference:
The Effect of CRLF injection also includes HTTP Request smuggling and HTTP Response Splitting. ( Detailing about them is out of the scope of this Blog, Maybe will discuss it in next blog post)
As I went through reports and write-ups, I compiled a cheat sheet for CRLF injection, covering different exploitation techniques. This serves as a quick reference for identifying and leveraging CRLF vulnerabilities in web applications.
CHEATSHEET
1. HTTP Response Splitting
HTTP response splitting occurs when an attacker injects CRLF (%0D%0A) into an HTTP response, allowing them to manipulate headers or inject new ones.
/%0D%0ASet-Cookie:mycookie=myvalue This injects a Set-Cookie header, which can be exploited for session fixation or altering user sessions.
2. CRLF Chained with Open Redirect
By combining CRLF injection with an open redirect vulnerability, attackers can manipulate response headers and force users to malicious destinations.
These payloads manipulate the Location header, forcing a redirection to an attacker-controlled site.
3. CRLF Injection Leading to XSS
CRLF injection can also be used to execute Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks by injecting headers like Content-Type and disabling security protections.
The first payload disables X-XSS-Protection, while the second injects a malicious script, leading to XSS execution.
4. Filter Bypass Techniques
Some applications implement filters to prevent CRLF injection, but attackers can bypass these protections using encoded characters.
Bypass Encoding:
Example Payload:
These Unicode-encoded sequences bypass input validation and inject malicious headers.
Result And Analysis
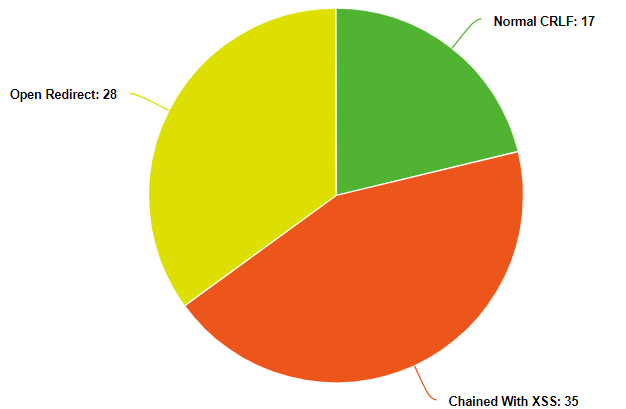
Most of the CRLF injection can lead to XSS and Open Redirects if chained properly which increases the Criticality of the report and you can escalate your report to Medium CVS score easily
Mitigation or Fix Implementation
A simple solution for CRLF Injection is to sanitize the CRLF characters before passing into the header or to encode the data which will prevent the CRLF sequences from entering the header.
Payloads
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/CRLF%20Injection
https://github.com/cujanovic/CRLF-Injection-Payloads/blob/master/CRLF-payloads.txt
Last updated